REED TYPE
POINTER TYPE
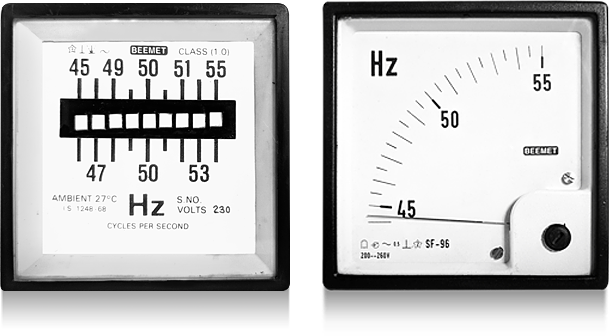
Beemet Frequencey meters are used to measure the applied frequency. They come as Pointer Type with built in Trasducer and Vibrating Reed Type.
Salient Features
• Vibrating Reed Type Frequency meters indicate the supply frequency by means of individual reeds, when
rated voltage+ 20% is applied across the terminals of the meter, the particular reed, whose natural
frequency of vibration coincides with the supply frequency, vibrates with full amplitude. In case the supply
frequency falls midway between two reeds both the reeds vibrate, at reduced amplitude. The amplitude
of vibration at the tip of reeds is high enough for a distint indication.
• The Pointer Type Frequency Meter has a clear, well defined scale marking at 90 degree angle. The pointer
indicates the applied frequency when voltage is applied across the terminals of the meter.
General Specifications
| Accuracy | ±1.5 / 2.0 of FSD |
| Measurable Quantities | AC and DC Voltage or Current |
| Pointer deflection | 0 - 90º |
| Frequency | 50/60Hz |
| Sensitivity | 1000Ω/V (Voltmeter); 2000Ω/V (ammeter) |
| Overload Capacity | According to IS: 1248 / IEC 51 |
| Short duration for voltmeter | 2 times for 5s: 1 overload 2 times for 0.5s: 9 overloads |
| Short duration for ammeter | 10 times for 5s: 1 overload 10 times for 0.5s: 9 overloads |
| Continiously | 1.2 times rated voltage or current |
| Operating Temperature | -10 to 55°C |
| Storage Temperature | -25 to 65°C |
| Relative Humidity | < 75% annaul average, non-condensing |
Range Chart
| Model | Description | Ammeter |
|---|---|---|
| SF - 72, 96 | Reed Type | 45-50-55 HZ, 47-50-53 HZ, 55-60-65 HZ |
| SP - 72, 96 | Pointer Type | 45-50-55 HZ, 47-50-53 HZ, 55-60-65 HZ |
Dimensions
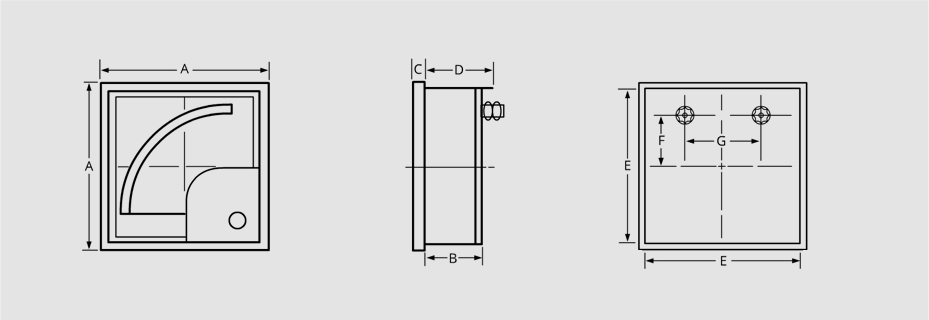
| Model | Dimensions (mm) | Scale Length | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | Panel Cutout | ||
| SF-72, SP-72 | 72 | 33 | 6 | 40 | 66 | 18 | 38 | 67x67 | 60 |
| SF-96, SP-96 | 96 | 33 | 6 | 41 | 90 | 30 | 40 | 91x91 | 90 |
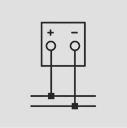
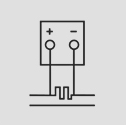
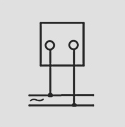
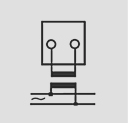
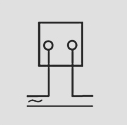
Wiring Diagrams
DC Moving Coil Voltmeter and Ammeters:
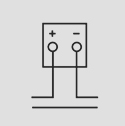
AC Moving Coil Voltmeter and Ammeters:

FAQ
Voltmeter is a device used to measure the electrical voltage in a circuit. It helps ensure that electronic devices receive the right amount of electrical push for proper operation and safety.
The types of frequency meters:
- Analog Frequency Meters
- Digital Frequency Counters
- Resonant Reed Frequency MetersOscilloscope with Frequency Measurement Handheld Frequency Meters
- Vibrating Reed Meters
A Hz meter also known as frequency meter is used to measure the frequency of signals, which is essential for applications requiring precise frequency analysis.
An analog frequency meter is used to display frequency readings using a needle or pointer by balancing two opposing forces, allowing it to measure frequencies accurately within its range.
A vibrating reed type frequency meter is made up of reeds that are tuned to a certain frequency. It measures frequency by matching the signal’s frequency when electricity is supplied and recording it.
A pointer type frequency meter records measurements using a moving pointer on a scale, indicating any changes in frequency through mechanical deflection. These meters are often categorized under analog meters.
