Analog panel meters are devices that display measurements of electrical parameters using a dial and a moving pointer. They have been widely used for decades and continue to be an essential tool in various industries. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to expand your knowledge, this blog will provide valuable insights into the operation, types, advantages, and applications of analog panel meters.
Components of Analog Panel Meters

1. Dial & Scale
The dial is the face of the meter with numbers and markings that show the measurements. The scale helps you read the values correctly.
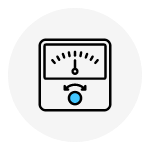
2. Pointer
The pointer is the moving part that shows the measurement on the dial. It moves along the scale to indicate the value of the parameter being measured.

3. Movement
The movement is the mechanism inside the meter that connects to the pointer. It responds to the electrical signals and makes the pointer move accordingly.

4. Magnets
Magnets create a magnetic field that interacts with the electrical signals in the meter. This causes the pointer to move and shows the measurement on the dial.

5. Pivot System
Magnets create a magnetic field that interacts with the electrical signals in the meter. This causes the pointer to move and shows the measurement on the dial.

6. Frame
Frame provides a protective casing for the internal components of the meter. It keeps the meter sturdy and safe from damage.
Operating Principle of Analog Panel Meters
Analog meters operate based on the electromagnetic induction principle.
1. Moving Coil Principle
Moving coil is the current-carrying coil placed in the meter. The coil is suspended in a magnetic field generated by permanent magnets or electromagnets. When an electric current flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field around it. The interaction between the magnetic field of the coil and the magnetic field of the meter causes the coil to rotate.
2. Force on the Moving Element
When the magnetic field is created, the moving coil moves in response to it. As it moves, it experiences a force. This force deflects the pointer attached to the moving element. The deflection of the pointer indicates the value of the measured parameter on the meter's scale.
3. Measurement Scale
The meter's scale is calibrated to provide accurate readings for the measured parameter. As the pointer moves along the scale, it aligns with the corresponding value of the measured parameter.
By utilizing these principles of electromagnetic induction, analog meters can measure electrical parameters and display them on meter’s dial.
Types of Analog Panel Meters
Here are some common types of analog panel meters designs for different parameters:
1. Ammeters
Measure the flow of current in Amperes in electrical circuits.
2. Voltmeters
Measure electrical potential difference in the circuit in volts (V).
3. Ohmmeters
Measure electrical resistance in ohms (Ω). Ohmmeters are used to test the resistance of components or circuits.
4. Frequency Meters
Frequenncy of an electrical signal is measured in Hertz.
5. Pressure Meters
Measure fluid or gas pressure. Pressure meters are utilized in various industries for monitoring and controlling pressure levels.
6. Level Meters
Measure the level of liquids or solids in tanks or containers. They find application in industries such as water treatment, agriculture, and manufacturing.
7. Wattmeters
Wattmeters monitor power consumption in electrical systems. They are measured in watts.
8. RPM Meters
Measure the rotational speed of machinery or motors. RPM meters are commonly used in automotive, industrial, and mechanical applications.
Features of Analog Panel Meters

1. Robust Construction
Built with durable materials, analog panel meeters are resistant to shock, vibration and other harsh environmental conditions.

2. Low Power Consumption
Analog panel meters require minimal power. They can be used in applications where power efficiency is a concern.

3. Wide Range of Measurement
Whether you want to measure values of high or low magnitude, analog meters can effectively do that as they support wide range of measurement.
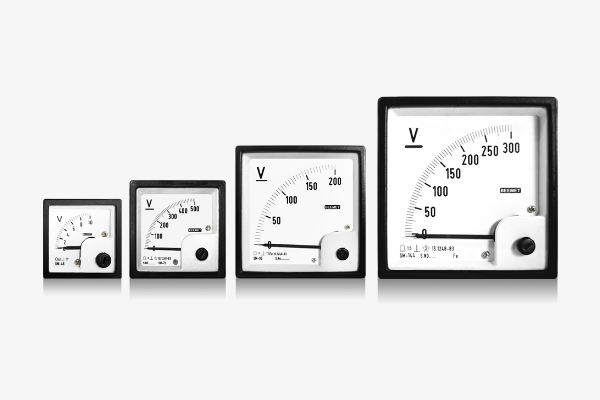
4. Versatile
Analog panel meters are versatile electrical instruments as they are compatible with both AC and DC signals.

5. Long Life
Analog meters have a long lifespan and can function efficiently for a long period of time without frequent repairs or maintenance.
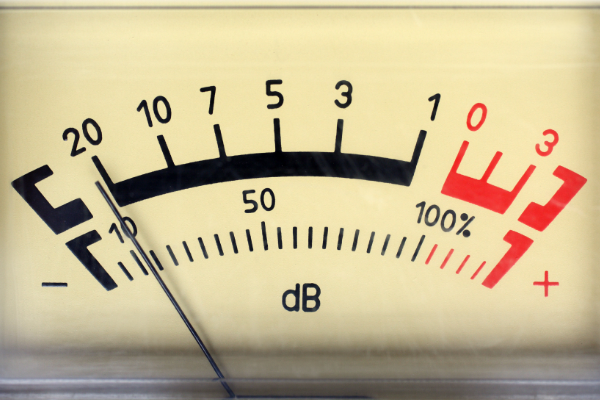

6. Direct Reading
Analog panel meters provide a direct visual readout through the movement of a pointer on a scale, allowing for quick interpretation of measurements.

7. Cost Effective
Analog panel meters are generally more affordable compared to digital meters, making them a go-to option for basic measurement requirements.
Applications of Analog Panel Meters

1. Industrial Machinery
Analog panel meters are used in industrial equipment to monitor voltage, current and power consumption.
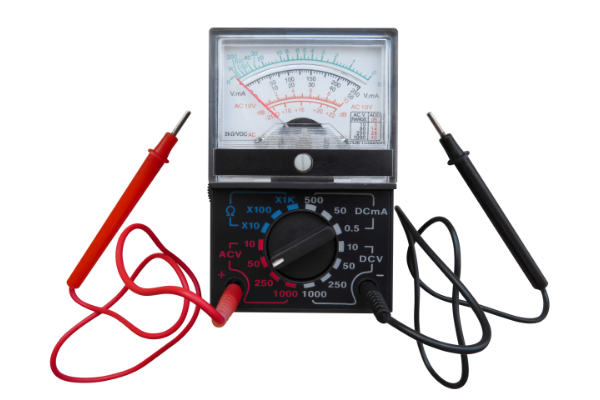

2. Remote Locations
Analog panel meters are unique as they can even operate without a power supply. Hence, they can be used in remote locations, off-grid systems or low-power environments.

3. Marine or Automotive Industries
When used in automotive and marine vehicles, analog panel meters can monitor engine parameters, fuel levels and speed.
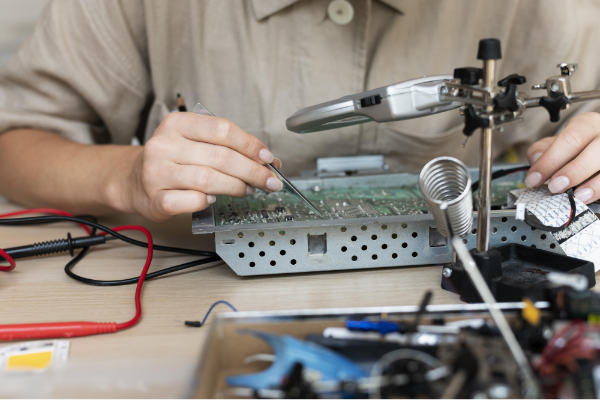
4. Testing & Troubleshooting
Analog panel meters are essential tools for electrical testing and troubleshooting, enabling quick and simple measurements of voltage, current, and resistance in circuits.
Difference Between Analog & Digital Panel meters
1. Display
A dial and point is used to indicate measurements on the scale in analog meters while digital panel meters use a digital display to indicate measurements.
2. Readability
In analog meters, you have to interpret the position of a moving pointer to get a proper reading. This is not the case with digital meters as they offer precise numerical readings and eliminate interpretation errors.
3. Accuracy
Analog Panel Meters have lower precision and accuracy compared to digital meters.
4. Additional Features
Analog meters do not provide any other feature apart from basic measurement. Digital Panel Meters offer advanced features like data logging, alarm communication interface and more.
Bottom Line
Analog meters offer simplicity, real-time response, and a direct visual interpretation of measurements. Despite the digital advancements, their durability, wide measurement range, and timeless charm make them valuable tools in various applications Explore a range of analog panel meters by BEEMET.
Recommended read- All you need to know about Digital Panel meters.
FAQs
Analog panel meters are used to measure and display electrical parameters including voltage, current and frequency. Using a moving needle or pointer on a dial, it shows the real time readings.
Types of analog instruments available includes:
- Ammeters
- Voltmeters
- Ohmmeters
- Frequency Meters
- Pressure meters
- Level meters
- Wattmeters
- RPM meters
Look at the position of the needle on the dial to read an analog meter. The pointed number is the measured value. If needle points between two numbers, approximate the value based on its position.
An analog meter uses a needle to indicate the current on the display thus providing continuous readings. Whereas digital meters show numerical values on the screen offering precise numerical outputs.
Analog meters offer durability and reliability in disturbing environments. They provide immediate visual feedback, thus being beneficial for quick assessments in multiple settings where rapid changes occur.
Some analog panel meters are capable of measuring multiple parameters simultaneously. This feature allows users to monitor different electrical quantities enhancing efficiency in various applications.
Analog meters are commonly used in industrial applications, control panels and laboratory equipment. They are used where quick visual feedback on electrical parameters are essential.



