DC Shunts are used in instances when the current is too large and cannot be measured by a panel meter or other instrument.
A DC shunt is a precision resistor designed to divert a known portion of current in a circuit. Unlike other types of shunts, such as AC shunts, which are used in alternating current applications, DC shunts are specifically designed for direct current systems. They are crucial in accurately measuring current and protecting sensitive components within an electrical circuit. DC shunts comprise a resistive element and are typically connected in parallel with a load.
Types of DC Shunts
DC shunts come in different types, each with unique characteristics and applications. Let’s explore three common types:

Wire-Wound Shunts
Wire-wound shunts are constructed using a high-grade resistive wire wound on a non-conductive core. These shunts are known for their high current-handling capabilities and low-temperature coefficients. They are commonly used in heavy-duty industrial systems, automotive applications, and large-scale electrical installations.
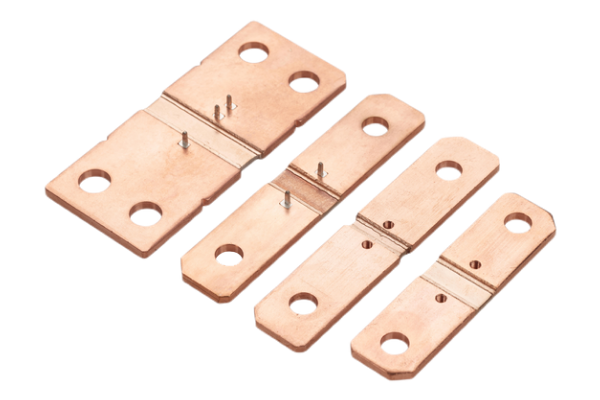
Manganin Shunts
Manganin shunts are made from an alloy composed of copper, manganese, and nickel. This alloy exhibits low-temperature coefficients and excellent long-term stability, making manganin shunts ideal for precision measurement instruments, laboratory equipment, and applications where high accuracy is paramount.

Solid-Shank Shunts
These shunts are made using metal bars or plates. Compact in size, solid shunts can be easily installed. Highly suitable for portable devices and small-scale electrical systems where the space is limited.
How to Use a DC Shunt?
- Before using a DC Shunt, know its current and voltage specifications.
- Connect the DC shunt in series with the circuit where you want to measure the current.
- Calculate the required shunt resistance based on the desired current measurement range and the shunt’s rated voltage drop. Use Ohm’s law (R = V/I) to determine the resistance value.
- Connect a voltage measurement instrument across the terminals of the shunt to measure the voltage drop across the shunt accurately.
Precautions While Using DC Shunts
- To ensure the longevity and proper functioning of the shunt, it is recommended to avoid using current levels that exceed 80% of the rated current for extended periods of time.
- When connecting the cable or copper bar of the primary loop of the shunt to the shunt itself, it is important to ensure there is no additional resistance introduced at the connection. Also, when sampling the secondary voltage, it should be done from the designated sampling point rather than a non-sampling point.
Advantages of DC Shunts
Accurate Current Measurement
Shunts provide a precise and reliable means of measuring electrical current. By diverting a known portion of current through the shunt, the resulting voltage drop can be measured and used to accurately determine the current passing through the circuit.

Cost-Effective Solution
Compared with other methods of current measurement, shunts are generally more cost-effective.
High Current Handling Capability
Shunts can handle high current levels. They are commonly used in applications where large currents need to be measured accurately, such as power generation, industrial equipment, and electric vehicle systems.
Wide Range of Applications
Shunts are used in power distribution systems, battery management systems, motor control, renewable energy systems, and many other electrical applications.

Simple Installation
Installing a shunt in a circuit is relatively straightforward. They can be easily connected in series with the load or power source, allowing for quick and hassle-free integration into the electrical system.

Low Voltage Drop
Shunts typically have low resistance values, resulting in minimal voltage drop across the shunt itself. This ensures that the shunt does not significantly affect the overall circuit performance and allows for accurate current measurement without significant power loss.
Long-Term Stability
Shunts, especially those made from high-quality materials like manganin alloy, offer excellent long-term stability. They exhibit low-temperature coefficients and resistive drift, ensuring accurate and consistent current measurements over extended periods of use.
Versatility
Shunts come in various types and sizes, allowing for flexibility in different applications. From heavy-duty wire-wound shunts for industrial systems to compact solid-shank shunts for portable devices, there is a wide range of options available to suit specific requirements.
Compatibility with Existing Systems
Shunts can be easily integrated into existing electrical systems without requiring major modifications. They can be connected to standard instrumentation and measurement equipment, making them compatible with commonly used tools and devices.
Overall, shunts provide an accurate, cost-effective, and versatile solution for current measurement in a wide range of electrical applications. Their high current handling capability, simplicity of installation, and compatibility with existing systems make them a preferred choice for many engineers and technicians.
For more details, check out our blog- “Shunts- All you need to know”
Applications of DC Shunts
- DC shunts are commonly employed in power generation systems to measure the current flowing through generators, alternators, and other electrical power sources.
- DC Shunts are used in heavy machinery, motors and control systems to prevent overloading and damage to the equipment.
- DC Shunts are also used in control panels, motor control centres and PLC to regulate current levels.
- In electrical safety systems, DC Shunts are used for ground fault detection and protection. Shunts help in preventing leakage and insulation breakdown.
- In measurement instruments like ammeters and voltmeters, shunts are used to measure current and power consumption.
- In solar power systems and wind turbines, DC shunts are utilized to measure the current produced by wind generators. This information is critical for assessing the efficiency of renewable energy systems, tracking power output, and optimizing energy harvesting.
Conclusion
DC Shunts are essential components for accurate current measurement in electrical circuits. Their high accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make them valuable in a wide range of applications, from power generation to transportation systems. By understanding their working principles, types, and proper usage, engineers can ensure precise current measurement, system performance monitoring, and informed decision-making.
Hope you enjoyed this Blog. If you are interested in similar blogs, checkout our dedicated blogs on Analog Panel meters & Digital Panel meter.
FAQ
A DC shunt is used to measure current in a circuit. As they are low-resistant, shunts allow a small portion of current to pass through it. This creates a voltage drop that can be measured accurately.
A Shunt is used to measure electric current by providing an accurate path to assess the flow of electricity. Shunts help in monitoring and controlling of electric systems.
A shunt motor gives high starting torque, has consistent speed under varying loads and is simple to control. These few features make shunt motors ideal for reliable performances.
DC shunts find applications in multiple fields including:
- Industrial Machinery
- Elevators and Lifts
- Cranes and Hoists
- Centrifugal Pumps
- Textile Industry
- Printing Machines
- Laundry Equipment
An electric shunt works by diverting a measured portion of current through its low-resistance path. The voltage drop across the shunt is proportional to the current flow, thus allowing accurate measurements.
DC Shunts are cost-effective as they provide precise current measurements without any need for complex circuitry. This results in less manufacturing and maintenance costs.