What is Current Transformer?
A current transformer is a device that helps in measuring alternating current. It converts high primary current to a low, safer level secondary current that is measurable.
A current transformer can be used to multiply or reduce alternating current. A typical current transformer is a series-connected electromagnetic device comprising an iron core, electrical grade lamination and copper wound coil.
Uses of Current Transformer
Measuring current transformers are widely used in electrical systems where direct current measurement is not practical or safe. A current transformer is typically used when the voltage or current is too high to directly measure. In this case, the CT performs its usual function of lowering the current.
The resultant lower or secondary current is suitable for processing into electronic equipment. In this way, by reducing the high current into an equivalent lower current, the actual electrical current flowing in an AC transmission line can be safely monitored. Hence, a current transformer is an indispensable part of an electronic power system.
CTs are also used to protect delicate measuring equipment. The current in the CT can be made significantly smaller than the current in the primary circuit being measured by increasing the number of windings.
Advantages of using CT Transformer
- Accurate Scaling: The current transformer function plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate scaling and protecting sensitive equipment by isolating high currents from measurement devices. Choosing current transformers means choosing accuracy. These devices precisely scale down high currents to levels suitable for measurement, ensuring precise and reliable readings.
- Safety: They allow measurement without direct contact with high currents, minimizing the risk of shocks and ensuring operator safety.
- Equipment Protection: By isolating measurement devices from high currents, they prevent damage and extend equipment lifespan.
- Reduced Power Loss: Current transformers contribute to efficient energy management. By enabling accurate measurements at lower currents, they help identify inefficiencies and reduce power wastage.
- Wide Application Range: Current transformers are versatile. They find applications in various industries, from power distribution to industrial automation, making them indispensable tools.
- Real-Time Insights: They provide real-time data, empowering operators to make informed decisions promptly.
- Compatibility: Current transformers are compatible with measurement instruments, like a universal remote control. They can easily interface with meters, relays, and other monitoring devices.
- Simplified Maintenance: They enable remote monitoring, reducing the need for frequent manual checks.
At BEEMET, we understand the significance of accurate current measurement. Our current transformers embody these advantages, ensuring precision, safety, and efficiency in various applications.
Maintenance of CT Current Transformer
Here are simple steps to ensure your current transformers stay in peak condition:
- Regular Inspection: Inspect current transformers periodically for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Promptly address any issues to maintain accurate measurements.
- Cleanliness: Dust and dirt can impact performance, so gently clean them when needed.
- Connection Check: Ensure that all connections are secure. Loose connections can lead to inaccurate measurements and impact device lifespan.
- Temperature Awareness: Ensure they operate within their specified temperature range to maintain accuracy
- Emergency Preparedness: Keep spare current transformers on hand in case of failures. This minimizes downtime and ensures uninterrupted operations.
How Does Current Transformer Work?
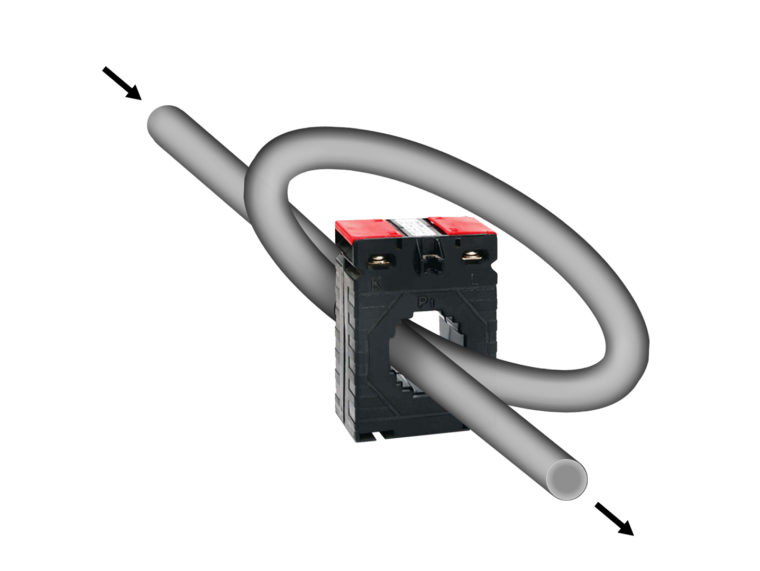
A current transformer CT operates on electromagnetic induction and plays a key role in converting high current into measurable values. The current transformer follows the principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. It is also referred to as low tension current transformer (LTCT) because it takes a low voltage and high current as input.
The CT comprises 2 windings – primary and secondary. The primary is wired to the power source, while the secondary is wired to the power distribution end. These two windings are twisted together around a single sealed magnetic iron circuit called the core, rather than being in electrical contact with each other.
The AC current flows through the primary winding. As per Faraday’s law, an equivalent magnetic flux is produced. This magnetic flux strikes the secondary winding and generates a proportionate alternating current.
The primary current flow is determined by a separate external load, while the secondary current is rated at 1A or 5A, making it suitable for measurement instruments.
Types Of Current Transformer:

Understanding the different current transformer types is essential for selecting the right one based on your system’s voltage, application, and installation requirements. Current transformers are grouped into numerous types based on characteristics such as their intended purpose, circuit voltage, mounting manner, and so on.
1. Indoor Current Transformers
Wound type, bar type, and window type transformers are the most common types of transformers used in low voltage circuits. Wound-type transformers have both primary and secondary windings, just like regular transformers
2. Outside Current Transformers
These are typically utilized for circuits with substantially greater voltages, such as switchyards and substations. These CTs are insulated with either oil or SF6 gas.
3. Bar Type Current Transformer
The primary winding of a bar-type current transformer is the actual cable or busbar of the primary circuit, which is equivalent to one turn. Higher-insulation bar types are available and are typically attached to the current-carrying device.
4. Wounds Current Transformer
This type of transformer has a primary winding on the core that is greater than one full round. The wound current transformer’s primary and secondary windings are separated by one or more turns encircling the core and are isolated from one another. Taps on the secondary winding allow them to be built as multi-ratio CTs. The wound type performs admirably across a broad working range.
The Difference Between CT And PT
1. Connection
The circuit is connected in series with a current transformer, allowing full line current to flow through the winding. Whereas a potential transformer is connected in parallel with the circuit, resulting in full line voltage across the winding.
2. Function
A current transformer decreases a high current to a safe and measurable level. Large primary currents are converted to little 1A/5A currents that can be measured with an ammeter.
Potential transformer measures and decreases high voltage values to lower ones. The high voltage is converted to a typical secondary voltage of 100V or less.
3. Windings
The primary winding of a current transformer has fewer turns and carries the current to be measured. The main/primary winding of a potential transformer has several turns and conveys the voltage to be measured.
The secondary winding of a current transformer has a significant number of turns on the secondary side and is connected to the instrument’s current winding. The secondary winding of a potential transformer contains a modest no. of turns on the other side and is connected to the device.
4. Value Of The Input
The input value of a current transformer is constant current, whereas the input value of a potential current transformer is constant voltage.
5. Winding Range
The range of a current transformer is 1A or 5A, while that of a potential transformer is 110V.
Factors to Consider While Selecting CT
2. It’s crucial to know which outputs your metering equipment can handle.
Applications Of Current Transformers
- Understanding current transformer application is essential for selecting the right CT for your system, whether for monitoring, protection, or metering. These transformers are used to monitor electric power in power plants, factories, grid stations, and industrial control rooms for metering and evaluating current flow in circuits and protection.
- It is utilized throughout the frequency response cycle to calculate harmonics and monitor power quality.
- It can be used in substation converters, HVDC projects, AC filters, and DC filters.
- In high-voltage mains and substations, current transformers are used as protection devices.
- It is utilised in capacitive banks as an integrated protection module.
- CTs with tiny footprints are used to detect current overloads, identify faults, and separate current feedback signals on printed circuit boards.
- In many three-phase systems, larger devices are utilized to measure current or voltage.
Hope you enjoyed this blog. If you’re seeking similar content on electrical instruments like Voltmeter, Ammeter, and Panel Meters, Beemet has you covered.
Also, If you are looking for high-quality current transformers, you can get in touch with us. Beemet is one of the top current transformers manufacturers in India. We specialize in the manufacturing of a wide range of electrical measuring instruments such as ammeters, voltmeters, shunts, and panel meters.
FAQs
A current transformer or Ct transformer is generally used to multiply or reduce the Voltage and current levels of a power supply. A Ct transformer is typically used when the Voltage or current is too high to measure directly. It follows the principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic Induction. A Ct consists of two windings – Primary and secondary. The primary is connected to a power source and the secondary is connected to the output end.
There are many types of current transformers one of which is a Bar current transformer. BEEMET Instruments offer a wide range of Bar current transformers and is one of the leading Current transformer manufacturers, Suppliers, and exporters in India
While selecting a CT, you should consider a variety of factors such as Cost efficiency, space efficiency, rated power, and your application need. They can be used for Industrial as well as domestic purposes. Current Transformers from BEEMET offers reliability and accuracy at an affordable cost, which makes them ideal for large industry application. Our CTs are welded properly and are unbreakable.
Current Transformers can be used for various applications, but the main application is measuring current and as a protection device. They can be used to measure current overload and identify faults in Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Also, CTs can be used to monitor electric power in power plants, factories, and grid stations.
For protection, they are used in capacitive banks, high-voltage mains, and substations. If you are looking for high-quality current transformers, you can get in touch with us. BEEMET is one of the top current transformers manufacturers, suppliers, and exporters in India.
Current transformers are grouped into numerous types based on characteristics such as their intended purpose, circuit voltage, mounting manner, and so on which are as follows: Indoor Current Transformers, Outside Current Transformers, Bar Primary Current Transformers and Wound Primary Current Transformers.
CT and PT are both Instrument transformers where CT stands for Current transformer and PT stands for Potential transformer (Voltage transformer). Both CT and PT are used to help the power system stay safe.
CT or Current transformer is a series-connected device that is mainly used to measure currents within equipment while PT or Potential Transformer is a parallel connected device used to measure relatively high voltage values. The output values in CT and PT are measured in Amperes(A) and Volts(V) respectively.
2. Vishal will be confirming the author’s bio by tomorrow. Once we receive it please get it implemented on all the blogs.
3. Vishal will also be sharing CT and digital panel meter videos. Please get it embedded on the blog and product page.
5. Add H2 – Our range of Current Transformers – Mention our product’s name with images here. Also, give them a backlink.
6. Give a link to the blog page using a section on the product page of the current transformer.
Step Up Transformer and Step Down Transformer.
Three Phase Transformer and Single Phase Transformer.
Electrical Power Transformer, Distribution Transformer and Instrument Transformer.
Two-Winding Transformer and Autotransformer.
Current transformers (CT) are connected in series with the conductor carrying that current, so it is effective for measuring current. Potential transformers (PT) are connected across an element, so they are effective for measuring voltage across that element.
Beemet is one of the top manufacturers of Current Transformers in India. Beemet has helped define a unique market for quality analog and digital measuring instruments used in the manufacturing and service industry.
In addition to CTs, we also manufacture other electrical measuring instruments such as ammeters, shunts, voltmeters, panel meters, etc.